
Calcium ions are also found dissolved in the sea water.Calcium is also the 5th most abundant element present in the human body.Calcium is the 5th most abundant element (by mass) found in the earth’s crust.Our teeth and bones contain calcium in it.Calcium is a very essential element for all living organisms.Interesting facts about calcium element are mentioned below. So the last electron of calcium enters the s-subshell or s-orbital. The simple answer: The elements will lie in the s, p, d or f block will completely depend upon the subshell in which the last electron will enter.įor example the electron configuration of calcium is 4s 2. How can you determine the blocks-wise position of elements? Protons 20 Neutrons 20 Electrons 20 Symbol Ca Atomic massĢ, 8, 8, 2 Electronic configuration 4s 2 Atomic radiusĢ31 picometers (van der Waals radius) Valence electronsĢ 1st Ionization energy 6.113 eV ElectronegativityįCC (Face centered cubic) Melting point 1115 K or 842 ☌ or 1548 ☏ Boiling point 1757 K or 1484 ☌ or 2703 ☏ Density 1.55 g/cm 3 Main isotope 40Ca Who discovered Calcium and when?īefore knowing this reason, first of all I want to ask you a simple question. Let’s dive right into it! Calcium Element (Ca) Information Appearanceĭull silvery grey color State (at STP) Solid Position in Periodic table So if you want to know anything about Calcium element, then this guide is for you. In fact, the table mentioned below is the perfect information box (Which gives you every single detail about the Calcium element in Periodic table.) 1999‑2023 - All Rights Reserved.This is a SUPER easy guide on Calcium element. Īlso see: The Orbitron: A gallery of atomic orbitals and a few molecular orbitalsĬopyright © Israel Science and Technology Directory.
#CA ELECTRON CONFIGURATION FULL#
The full story of the electron configurations of the transition elements.
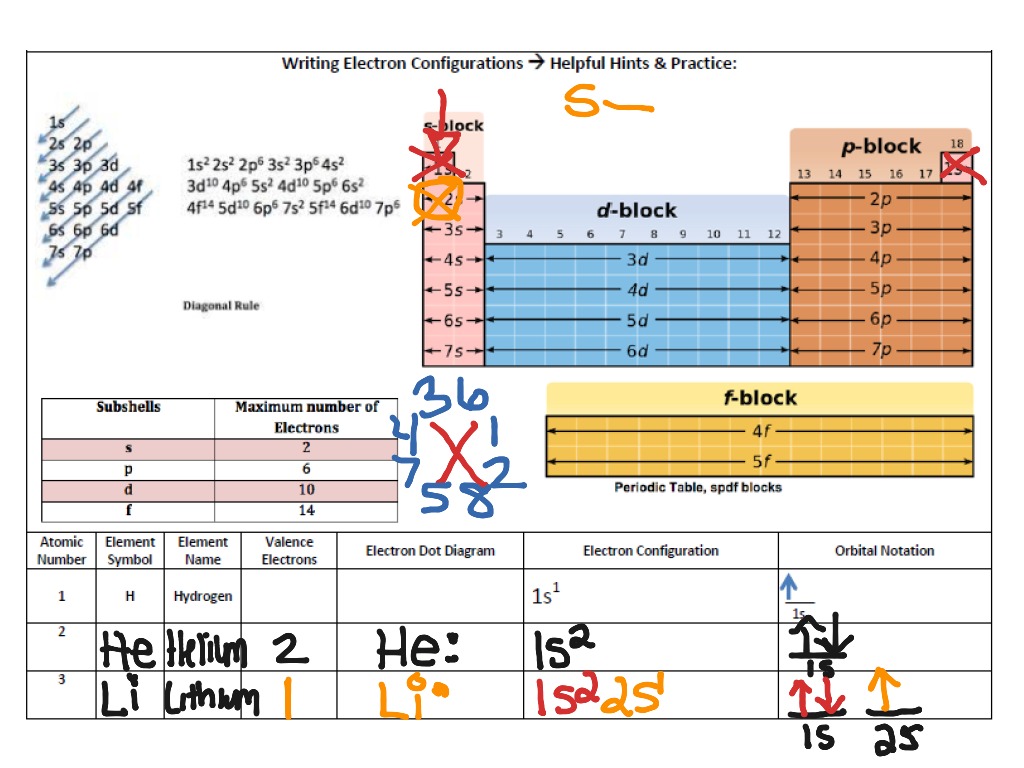
Thus, each proton and neutron has a mass of about 1 amu. This isotope of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons. Atomic mass is measured in Atomic Mass Units (amu) which are scaled relative to carbon, 12C, that is taken as a standard element with an atomic mass of 12. Each element is uniquely defined by its atomic number.Ītomic mass: The mass of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom. The table below shows the full forms of the electron configurations of noble gases. For an explanation of these aspects, see the reference by Schwarz listed below. Thus, the electron configuration of Sc is 3d 1 4s 2. Starting with Scandium (Sc, atomic #21), the 3d orbital has a lower energy than the 4s. Energy levels and sublevels Principal energy level Therefore, orbital 4s is filled with electrons prior to orbital 3d.
The reason for this is that the energy level of orbital 4s is slightly lower than that of orbital 3d.

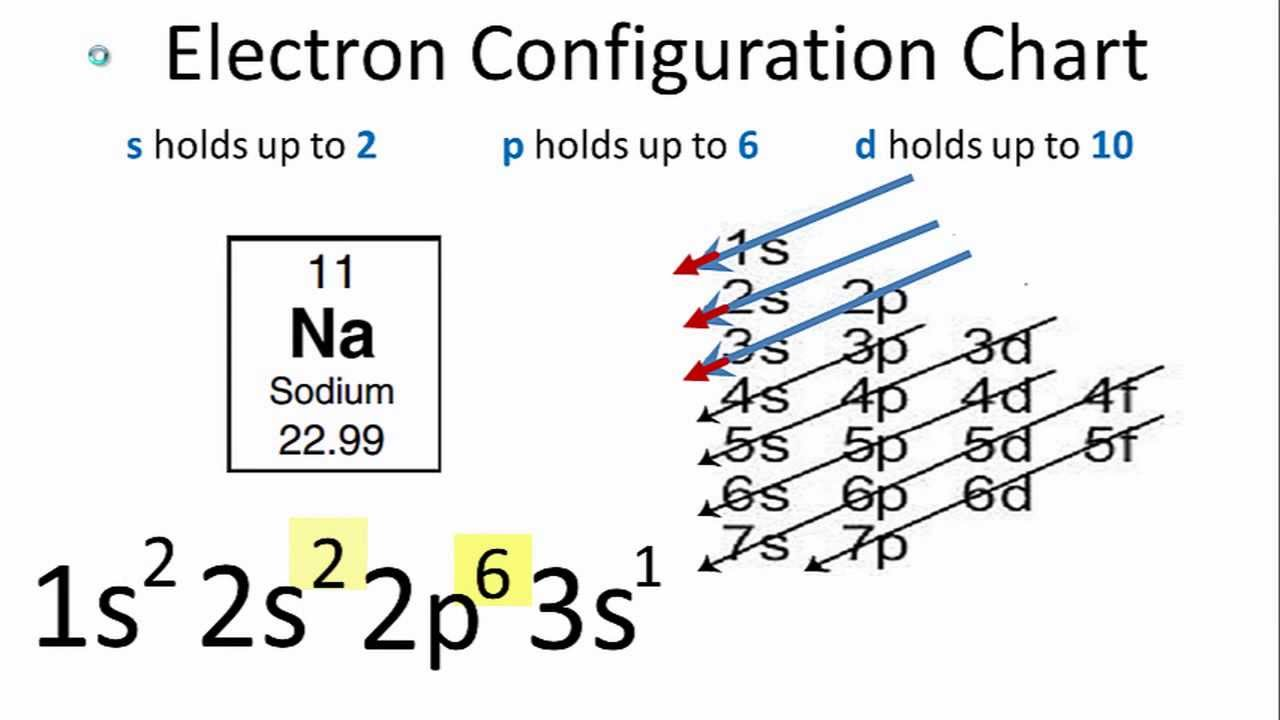
Note that in the electron configuration of both K and Ca, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital. The one additional electron configuration completes the picture for 19 electrons of Potassium.
#CA ELECTRON CONFIGURATION PLUS#
The abbreviated form - 4s 1 - means the electron configuration of Argon (Ar), plus one electron in the 4s orbital. The full electron configuration of Potassium (K) is 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 64s 1. Thus, the configuration shown for Potassium is 4s 1 (see Table below). Thus, substituting the config of He gives the full config for Neon: 1s 22s 22p 6įor example, for Potassium (K) (atomic #19), the preceding noble gas is Argon (Ar) (atomic #18). For example, the abbreviated configuration for Neon is 2s 2 2p 6. In the periodic table beyond Helium (He), each element's electron configuration is shown in an abbreviated form that starts with the symbol of the noble gas that precedes it. The superscript shows that there is one electron in the 1s orbital. The simplest configuration is for Hydrogen: 1s 1. An atom's electron configuration describes the distribution of its electrons in the atomic orbitals ordered by the orbitals' energy levels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
